PCIe 5.0 PHY in TSMC (16nm, 12nm, N7, N6, N5, N4P, N3E, N3P)
You are here:
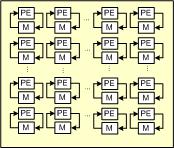
Variable FFT (run time choice of FFT size)
This FFT circuit employs unique architectural characteristics, different than any other FFT implementation. In particular the locality, simplicity and regularity of the processing core keeps interconnect delays lower than cell delays, leading to clock speeds that can approach the FPGA fabric limitations, e.g., "worst case" Fmax speeds >500MHz in 65nm FPGA technology. Short critical path lengths also lower power dissipation. Additionally, a novel algorithm reduces the number of cycles needed per FFT to less than the transform size. Because the circuit is a "memory based" architecture it is programmable so that a range of transform sizes (even non-powers of 2) can be performed on the same array given adequate memory resources. Finally, it includes a low overhead hybrid floating-point feature that increases dynamic range for a given fixed-point word size.
查看 Variable FFT (run time choice of FFT size) 详细介绍:
- 查看 Variable FFT (run time choice of FFT size) 完整数据手册
- 联系 Variable FFT (run time choice of FFT size) 供应商
Block Diagram of the Variable FFT (run time choice of FFT size)

