HEVC/AVC Single-core Video Codec HW IP of Low-cost Version: 4K60fps
You are here:
OFDM synchronization unit
Noesis Technologies ntSYNC is a fully programmable component used to achieve time and frequency synchronization in OFDM technology physical layer implementations. It interfaces directly with the physical layer’s front-end (line/RF) interface and using a cross-correlation proprietary algorithm to find the starting point of a received data frame. The generic design approach as well as a number of pre-processed optimizations allow for integration to any OFDM compliant physical layer.
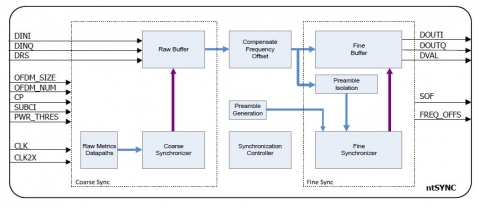
The front-end interface feeds the ntSYNC with received signal above a certain power level via the DINI/DINQ ports and flags the signal as valid (DRS). The signal is buffered temporarily in Raw Buffer until raw synchronization phase takes place. The raw synchronization algorithm searches for received power level equal to the a-priori known preamble power levels. The power levels can be programmed via the PWR_THRES input port.
Once raw synchronization is achieved the estimated location of the preamble is decided and the coarse synchronization phase begins. Coarse synchronization searches the preamble estimated location more closely with correlative metrics, approximates the received frames starting point and calculates the channels frequency offset shift on the received signal. The raw buffer discards data before the approximated synchronization point and propagates the rest of the signal to the frequency offset compensation unit. The results are being stored in the fine buffer. Additionally the estimated preamble data are being isolated.
The isolated preamble is correlated against the known generated preamble by the fine synchronization process. Fine synchronization decides the final synchronization point and discards all previous data in the fine buffer. The programmable OFDM control parameters such as cyclic prefix size (CP), sub-channelization operation (SUBCI), the size of the OFDM symbol (OFDM_SIZE) and the number of OFDM symbols that are expected to be included in the received frame (OFDM_NUM) are required in order to decide the end of the received frame, once the synchronization point has been calculated.
The front-end interface feeds the ntSYNC with received signal above a certain power level via the DINI/DINQ ports and flags the signal as valid (DRS). The signal is buffered temporarily in Raw Buffer until raw synchronization phase takes place. The raw synchronization algorithm searches for received power level equal to the a-priori known preamble power levels. The power levels can be programmed via the PWR_THRES input port.
Once raw synchronization is achieved the estimated location of the preamble is decided and the coarse synchronization phase begins. Coarse synchronization searches the preamble estimated location more closely with correlative metrics, approximates the received frames starting point and calculates the channels frequency offset shift on the received signal. The raw buffer discards data before the approximated synchronization point and propagates the rest of the signal to the frequency offset compensation unit. The results are being stored in the fine buffer. Additionally the estimated preamble data are being isolated.
The isolated preamble is correlated against the known generated preamble by the fine synchronization process. Fine synchronization decides the final synchronization point and discards all previous data in the fine buffer. The programmable OFDM control parameters such as cyclic prefix size (CP), sub-channelization operation (SUBCI), the size of the OFDM symbol (OFDM_SIZE) and the number of OFDM symbols that are expected to be included in the received frame (OFDM_NUM) are required in order to decide the end of the received frame, once the synchronization point has been calculated.
查看 OFDM synchronization unit 详细介绍:
- 查看 OFDM synchronization unit 完整数据手册
- 联系 OFDM synchronization unit 供应商
Block Diagram of the OFDM synchronization unit

Wireless communications IP
- Multi-protocol wireless plaform integrating 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), Bluetooth 5.4 Dual Mode, 802.15.4 (for Thread, Zigbee and Matter)
- WiGig Wireless Display Codec
- Peak Cancellation Crest Factor Reduction (PC-CFR)
- IEEE 802.3 Clause 74 FEC
- Wi-Fi 802.11 ax/Wi-Fi 6 /Bluetooth LE v5.4/15.4-2.4GHz RF Transceiver IP for IOT Application in TSMC22 ULL
- OFDM Modem






