You are here:
Low-power, low-gate-count, highly-configurable DSP core for audio and control processing
TinyCore is a DSP core that supports stream-based processing of time domain audio or control data samples including single cycle multiply-adds and multiply-subtracts. With built in support for sample delay memory of varying size and automatically saturating arithmetic instructions, TinyCore makes it possible to implement a bi-quad filter in five instructions.
TinyCore is provided as a reconfigurable RTL model that permits synthesis of FPGA and ASIC gate-level netlists with a wide range of configurable parameters that can be selected for the needs of the application. From low-cost ICs demanding the smallest gate count, through to top-end pro-audio systems, TinyCore can be configured to give the performance you require.
Any combination of these parameters can be used:
• 1 - 32 audio I/O channels
• data path bit width from 16 to 48 bits
• 128 - 8192 instructions per audio sample period
• 1 - 3 data storage RAMs, each containing between 32 and 4096 data words
• optional external memory interface for effects requiring large delays (e.g. sparse FIR filters, reverbs)
• support for encrypted code so that effects can be used securely
TinyCore makes no assumptions on master clock frequency and so is independent of audio sample rate. It is optimised for low power and low gate count through a configurable memory access method and a split multiplier design.
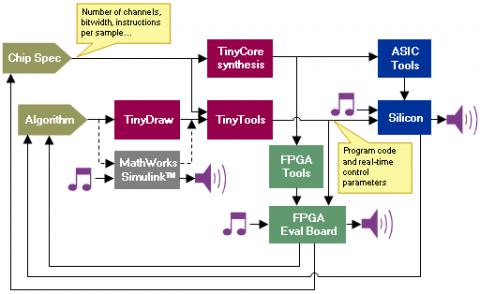
For programming TinyCore, a suite of tools have been developed to achieve rapid prototyping and development and highly efficient implementation of DSP algorithms. TinyTools are centred on a graphical programming environment and the TinyDraw front-end allows the DSP engineer to visually create algorithms in a fast, intuitive manner.
Once designed, the DSP design is then optimised using TinyOpt. This ensures the maximum processing can be squeezed into any given TinyCore, and will allow the minimum specification TinyCore to be used, which ultimately saves gate count. TinyOpt utilises a twenty three pass optimisation to remove all unnecessary instructions to the point where it beats even Oxford Digital’s best assembly level experts by ~10%.
TinyTools then applies its very own assembler, TinyAsm, to create code that is ready to be loaded and executed straight away on TinyCore development hardware within seconds of completing a DSP schematic.
Once the DSP is running on TinyCore, coefficients in the DSP design can be adjusted using TinyGcon. Real-time control ensures easy and precise fine-tunings can be made to the algorithm, with the results immediately observable by listening and/or measurement.
Simulink-2-Tiny allows users of MathWorks Simulink (R) to replace TinyDraw. A blockset of TinyCore instructions is provided, which will produce bit-accurate simulation when run. An extraction tool then takes the DSP algorithm from the Simulink model, which allows the standard TinyTools suite to be run on the design, including the powerful TinyOpt optimising compiler.
TinyCore is provided as a reconfigurable RTL model that permits synthesis of FPGA and ASIC gate-level netlists with a wide range of configurable parameters that can be selected for the needs of the application. From low-cost ICs demanding the smallest gate count, through to top-end pro-audio systems, TinyCore can be configured to give the performance you require.
Any combination of these parameters can be used:
• 1 - 32 audio I/O channels
• data path bit width from 16 to 48 bits
• 128 - 8192 instructions per audio sample period
• 1 - 3 data storage RAMs, each containing between 32 and 4096 data words
• optional external memory interface for effects requiring large delays (e.g. sparse FIR filters, reverbs)
• support for encrypted code so that effects can be used securely
TinyCore makes no assumptions on master clock frequency and so is independent of audio sample rate. It is optimised for low power and low gate count through a configurable memory access method and a split multiplier design.
For programming TinyCore, a suite of tools have been developed to achieve rapid prototyping and development and highly efficient implementation of DSP algorithms. TinyTools are centred on a graphical programming environment and the TinyDraw front-end allows the DSP engineer to visually create algorithms in a fast, intuitive manner.
Once designed, the DSP design is then optimised using TinyOpt. This ensures the maximum processing can be squeezed into any given TinyCore, and will allow the minimum specification TinyCore to be used, which ultimately saves gate count. TinyOpt utilises a twenty three pass optimisation to remove all unnecessary instructions to the point where it beats even Oxford Digital’s best assembly level experts by ~10%.
TinyTools then applies its very own assembler, TinyAsm, to create code that is ready to be loaded and executed straight away on TinyCore development hardware within seconds of completing a DSP schematic.
Once the DSP is running on TinyCore, coefficients in the DSP design can be adjusted using TinyGcon. Real-time control ensures easy and precise fine-tunings can be made to the algorithm, with the results immediately observable by listening and/or measurement.
Simulink-2-Tiny allows users of MathWorks Simulink (R) to replace TinyDraw. A blockset of TinyCore instructions is provided, which will produce bit-accurate simulation when run. An extraction tool then takes the DSP algorithm from the Simulink model, which allows the standard TinyTools suite to be run on the design, including the powerful TinyOpt optimising compiler.
查看 Low-power, low-gate-count, highly-configurable DSP core for audio and control processing 详细介绍:
- 查看 Low-power, low-gate-count, highly-configurable DSP core for audio and control processing 完整数据手册
- 联系 Low-power, low-gate-count, highly-configurable DSP core for audio and control processing 供应商
Block Diagram of the Low-power, low-gate-count, highly-configurable DSP core for audio and control processing

Low-power IP
- Ultra low-power crystal-based 32 kHz oscillator designed in TSMC 22ULL
- 2.5D Multi-Core Raster & Vector Graphics Processor for low-power SoCs with Microcontroller
- Low-Power Combo Bandgap Voltage and Current References (1.21V/600nA) - GlobalFoundries 0.13um BCD
- Low-Power Wide Range PLL - UMC 130 L130EHS
- Ultra low-power 2.4 GHz transceiver for Bluetooth Low Energy 5
- Low-power 32-bit RISC-V processor








