You are here:
2.5Gb Ethernet MAC
The 2.5Gb MAC core can support data rates of 1Gbps or 2.5Gbps in LatticeSC/M™ devices. The 2.5Gb MAC transmits and receives data between a host processor and an Ethernet network. The main function of the Ethernet MAC is to ensure that the Media Access rules specified in the 802.3 IEEE standards are met while transmitting and receiving Ethernet frames.
The data received from the GMII interface is first buffered until sufficient data is available to be processed by the Receive MAC (Rx MAC). The Preamble and the Start of Frame Delimiter (SFD) information are then extracted from the incoming frame to determine the start of a valid frame. The Receive MAC checks the address of the received packet and validates whether the frame can be received before transferring it into the FIFO. Only valid frames are transferred into the FIFO. The 2.5Gb MAC however always calculates CRC to check whether the frame was received error-free or not.
The data received from the GMII interface is first buffered until sufficient data is available to be processed by the Receive MAC (Rx MAC). The Preamble and the Start of Frame Delimiter (SFD) information are then extracted from the incoming frame to determine the start of a valid frame. The Receive MAC checks the address of the received packet and validates whether the frame can be received before transferring it into the FIFO. Only valid frames are transferred into the FIFO. The 2.5Gb MAC however always calculates CRC to check whether the frame was received error-free or not.
查看 2.5Gb Ethernet MAC 详细介绍:
- 查看 2.5Gb Ethernet MAC 完整数据手册
- 联系 2.5Gb Ethernet MAC 供应商
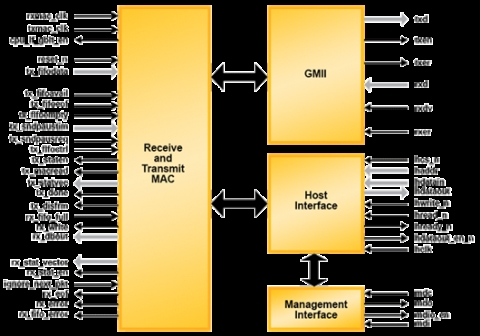
Block Diagram of the 2.5Gb Ethernet MAC

FPGA IP
- RT-630-FPGA Hardware Root of Trust Security Processor for Cloud/AI/ML SoC FIPS-140
- Complete USB Type-C Power Delivery PHY, RTL, and Software
- Ethernet TSN Switch IP Core - Efficient and Massively Customizable
- CXL 2.0 Agilex FPGA Acclerator Card
- PCIe Gen3 to SRIO Gen3 Bridge (FPGA)
- 65nm/40nm Low Power eFPGA IP and Open Source FPGA Software
